14 Weeks Pregnant Belly When Can I Feel Uterus
- 1 week pregnant
- 2 week pregnant
- 3 week pregnant
- 4 week pregnant
- 5 week pregnant
- 6 week pregnant
- 7 week pregnant
- 8 week pregnant
- 9 week pregnant
- 10 week pregnant
- 11 week pregnant
- 12 week pregnant
- 13 week pregnant
- 14 week pregnant
- 15 week pregnant
- 16 week pregnant
- 17 week pregnant
- 18 week pregnant
- 19 week pregnant
- 20 week pregnant
- 21 week pregnant
- 22 week pregnant
- 23 week pregnant
- 24 week pregnant
- 25 week pregnant
- 26 week pregnant
- 27 week pregnant
- 28 week pregnant
- 29 week pregnant
- 30 week pregnant
- 31 week pregnant
- 32 week pregnant
- 33 week pregnant
- 34 week pregnant
- 35 week pregnant
- 36 week pregnant
- 37 week pregnant
- 38 week pregnant
- 39 week pregnant
- 40 week pregnant
- 41 week pregnant
- 42 week pregnant
You have started your second trimester. Now, you will probably feel much better. Most often, this is a comfortable phase for a pregnant woman because her belly is not too big yet, she does not suffer from insomnia at night, and she finds food delicious and smells pleasant again.
Congratulations! The first stage is over. Now that you are entering the second trimester, your body has started changing — the uterus has increased in size, and your belly is rounding out slightly.
As the unpleasant first trimester symptoms disappear, you feel more energetic again. It is high time you enjoyed your new status.
Your baby at week 14 of pregnancy
How big is your baby at 14 weeks pregnant?
The weight of the fetus is approximately 0.8–1.2 oz (25–35 g).
The length is 3.1–3.9 in (8–10 cm).
Your baby has reached the size of a peach or lemon.
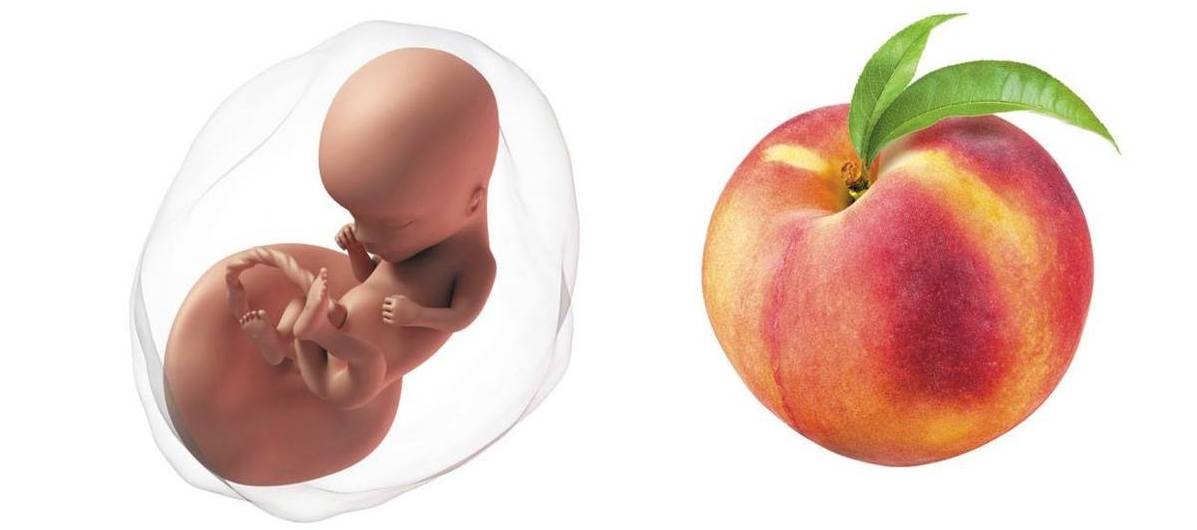
Pregnancy week 14 fetal development
Your baby at week 14:
- is moving their arms and legs actively
- can suck their finger
- can turn their head
What is new in this period?
- The grasp reflex is evolving. In response to a touch, the baby will try to grab an object. They can touch the umbilical cord and the fetal membrane.
- The baby's eyebrows and eyelashes start growing; their facial features are being formed. Their facial muscles are working better. Now, the little one is able to smile.
- Their joints are developing; their movements are becoming more coordinated.
- The baby's neck muscles are getting stronger. Their head is not dropping forward anymore.
- The little one is developing a unique pattern on their fingers (fingerprints), which will be completely formed by week 24.
- Their body is covered by lanugo — thin downy hairs. By the end of your pregnancy, they will have almost completely disappeared.
Breathing
Since their lungs are not functioning yet, the little one "breathes" with the help of the placenta. The respiratory system already began developing at the end of the first month; now, it is evolving actively. Ultrasound can show fetal respiratory movements (appearing at weeks 12–20). They improve blood circulation but do not lead to lung expansion.
During respiratory movements, the glottis is closed; therefore, the amniotic fluid that the baby swallows goes back or dissol
Internal organs
As the baby develops, their internal organs begin to work:
- their liver is performing the digestive function — producing bile.
- their kidneys are producing urine, which is excreted into the amniotic fluid.
- their spleen is producing red blood cells (erythrocytes); their bone marrow starts forming blood, too.
It is already possible to determine the baby's blood type and even Rh factor.
During this period, their body starts to release hormones:
- insulin from the fetal pancreas
- thyroid hormones from the fetal thyroid gland (weeks 14–15)
In boys, the prostate is actively producing testosterone. In girls, the ovaries have shifted to the pelvis.
Blood circulation
Now, the baby is getting different substances from the mother through the placenta, which is how it will remain until they are born.
Blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients flows through the veins of the umbilical cord to the baby, nourishing their organs and tissues.
Then, from the fetus, it enters the arteries of the umbilical cord and flows through them to the placenta. There, the blood is purified and enriched again and before returning to the fetus.
The blood of the mother and baby does not mix; it can differ in group and Rh factor, among other things.
The fetal blood circulation is significantly different from that of a newborn. Since the fetus' lungs are not functioning yet, they are not supplied with blood as actively as after childbirth.
The baby's reactions
Your baby can already respond to your mood: they get excited if you are nervous, and rejoice when you feel good.
At the moment, this is only visible via ultrasound, which lets you observe the reaction of your little one. In a few weeks, you will be perfectly aware of their responses without any devices because you will feel your baby moving and stirring.
It is important that you learn to deal with stress. This will help your child acquire this vital skill in the future.
Your body at week 14 of pregnancy
You are actively gaining weight. This occurs due to an increase in blood and lymph volume.
The recommended amount of weight gain depends on your pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). If it was within the normal range, doctors suggest gaining 0.7–1.1 lbs (350–500 g) per week in the second trimester.
If your BMI was above or below the norm, or if you lost or put on a fair amount of weight during the first trimester, your healthcare provider will draw up an individual weight gain plan for you.
Now is the time to find a physical activity you really enjoy, that is safe during pregnancy, and start exercising.
Your veins are becoming more prominent. As the pregnancy progresses, you may notice veins popping up on your legs, abdomen, and breasts. These changes are mainly physiological.
However, if your leg veins have become irregularly enlarged or developed bumps, this may indicate varicose veins, which can surface at any point throughout pregnancy.
This also has to do with genetic predisposition.
What can help prevent varicose veins from progressing further?
- Weight control — follow your doctor's individual weight gain recommendations; extra pounds will put even more strain on the circulatory system, which is already operating at an enhanced capacity.
- A balanced diet — a diet rich in vitamin C will help support your veins as they experience increased pressure.
- Physical activity — regular exercise improves muscle tone in the legs and ensures that blood flows in the correct direction through the veins; try attending prenatal classes or walking more often.
- Reducing pressure on the legs — keep your legs up when sitting or lying down; avoid standing up for a long time and sitting cross-legged.
- Comfortable clothing — your clothes and shoes shouldn't be too tight
- Compression stockings — this type of hosiery helps reduce pressure on venous walls throughout pregnancy and even during labor; there are different compression degrees for preventing and treating varicose veins.

14 weeks pregnant belly
At 14 weeks of pregnancy, your uterus has expanded to fill your pelvis and ascend into your abdominal cavity — you may be able to feel your baby bump as a soft, smooth oval.
14 weeks pregnant symptoms
Nausea and morning sickness go away. The placenta is almost fully formed, while vascular system changes associated with this stage are coming to a close. Your psychological and emotional state is balancing out, mood swings becoming increasingly rare. You may even feel a surge of strength and energy, as well as readiness to get back to your usual lifestyle. Feel free to enjoy this quiet phase.
Your appetite increases. To stay well, try to pay more attention to your diet. It should contain enough protein, carbohydrates, fats, and fiber. Enjoy your food in small and regular meals. It is best that you avoid high-sugar foods.
You become more susceptible to colds. Nature makes sure that the baby is as safe as possible in the womb. Your immune system is suppressed so that the developing fetus is not rejected by your body. Despite the fact that infection no longer poses as much threat as in the first trimester, try to take good care of yourself by:
- spending less time in public places during the cold and flu season
- avoiding contact with sick people
- washing your hands often or carrying hand sanitizer
If you still catch a virus, consult your doctor, who will prescribe the treatment that is right for you.
You may develop a stuffy nose. High estrogen and progesterone levels contribute to boosting blood flow to mucous membranes (including that of the nasal cavity), making them swell up and soften.
-
If you have faced this problem, try humidifying the air in your house more often to make breathing easier.
14 weeks pregnant ultrasound: do you need it?
In most countries, the first scan of a pregnant woman takes place between weeks 8 and 14. It's usually followed by another scan at 18-21 weeks. This is sometimes referred to as a dating scan because it will give you a reliable idea of your expected due date (EDD) and also confirm how many babies you're carrying!
14 weeks pregnant lifestyle
Your pregnancy may be a challenging time for you, but do your best to follow a healthy lifestyle. This will provide the best support for you and your baby until full term. Your diet should contain a wide variety of foods from all the recommended food groups, including a mixture of fresh fruit and vegetables whenever possible. You should also aim to drink between 6 and 8 8-ounce glasses of water each day.
Sex at week 14 of pregnancy
Unless your doctor has told you otherwise, your sex life can continue as normal throughout pregnancy.
What to expect at 14 weeks pregnant — checklist
Normally, there are no must-take tests at week 14.
In the next few weeks of the second trimester, you will have to:
- take a marker screening blood test (weeks 15–20)
- undergo ultrasound screening (weeks 18–20)
- take a glucose tolerance test (weeks 24–28)
https://www.webmd.com/baby/guide/your-pregnancy-week-by-week-weeks-13-16#1
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/14-weeks-pregnant/
https://www.nhs.uk/start4life/pregnancy/week-by-week/2nd-trimester/week-fourteen/
14 Weeks Pregnant Belly When Can I Feel Uterus
Source: https://flo.health/pregnancy/week-by-week/14-weeks-pregnant
0 Response to "14 Weeks Pregnant Belly When Can I Feel Uterus"
Post a Comment